Trending Applications of sugar cane products in Today’s Market
Trending Applications of sugar cane products in Today’s Market
Blog Article
Discover Everything About Sugar Cane: From Production Methods to Item Innovations
Sugar cane is a crop with both historical value and contemporary importance. Its cultivation has evolved from conventional techniques to contemporary techniques that fulfill today's farming demands. This development includes cutting-edge processing strategies that change the cane right into a selection of products. As the industry encounters environmental obstacles, new lasting methods are arising. The intricacies of sugar cane production and its future in global markets existing fascinating questions worth exploring even more.
The Background of Sugar Cane Growing
Sugar cane is commonly connected with exotic environments, its cultivation has an abundant background that dates back thousands of years. Stemming in Southeast Asia, the earliest records of sugar cane's usage go back to around 8000 BCE, where it was chewed for its sweet taste. By the first millennium, it spread out to India, where it ended up being integral to neighborhood societies. The modern technology to take shape sugar emerged in India by the 5th century CE, marking a considerable landmark in sugar production.With the growth of trade routes, sugar cane located its means to the Middle East and, at some point, Europe. The facility of vineyards in the Caribbean during the 16th century changed the worldwide sugar market, driven greatly by early american expansion. As sugar came to be an in-demand commodity, its farming formed economies and cultures, preparing for modern manufacturing methods that developed with the innovation of farming and technology.
Conventional Farming Methods
As sugar cane cultivation developed through history, conventional farming techniques became fundamental techniques that shaped its manufacturing. These methods, usually given via generations, consisted of the usage of manual devices such as hoes and machetes for planting and harvesting. Farmers commonly prepared the soil by hand, making use of plant rotation and intercropping to keep dirt fertility and control pests. Water administration was essential, with several standard farmers counting on natural watering systems and rain harvesting.Planting was oftentimes to correspond with seasonal rainfalls, assuring ideal development conditions. Commonly, sugar cane was planted in rows, permitting less complicated maintenance and harvesting. Harvesting was done by hand, requiring competent labor to reduce damages to the stalks. On the whole, traditional farming techniques highlighted sustainability and a deep understanding of the neighborhood environment, creating a crucial part of the cultural heritage surrounding sugar cane agriculture. These techniques prepared for future improvements in sugar manufacturing.
Modern Agricultural Practices
Modern agricultural techniques have progressively incorporated precision farming techniques to improve sugar cane manufacturing. sugar cane products. These methods use data-driven methods to maximize inputs and improve yields while lessening environmental influence. In addition, sustainable pest administration strategies are being taken on to shield crops without jeopardizing ecological equilibrium
Precision Farming Strategies
Precision farming strategies represent a transformative strategy to agriculture, leveraging innovation to enhance productivity and sustainability in sugar cane manufacturing. By using tools such as GPS, remote picking up, and information analytics, farmers can keep track of plant health, dirt problems, and water use with unmatched accuracy. This data-driven technique permits targeted interventions, decreasing waste and maximizing source allowance. Drones and satellite images promote real-time evaluations, making it possible for farmers to react promptly to arising problems or adjustments in environmental conditions. In addition, precision farming improves yield forecasting and improves decision-making processes, inevitably leading to much better plant administration. Consequently, sugar cane manufacturers can achieve greater efficiency and productivity while decreasing their ecological footprint, contributing to the general development of contemporary farming practices.
Sustainable Insect Administration
Reliable management of bugs is vital for preserving the health and productivity of sugar cane crops. Lasting insect monitoring methods concentrate on lessening chemical inputs while making best use of eco-friendly equilibrium. sugar cane products. Integrated Bug Administration (IPM) is a prominent technique, integrating biological control, environment control, and the usage of immune sugar cane varieties. Farmers are significantly employing valuable insects and all-natural killers to suppress parasite populations, decreasing reliance on synthetic pesticides. Tracking pest degrees with catches and searching permits timely treatments, making sure that control actions are used just when necessary. Additionally, plant turning and intercropping boost biodiversity, more decreasing bug episodes. By embracing these sustainable techniques, sugar cane producers can maintain crop yield while promoting ecological stewardship and decreasing the adverse influences connected with traditional parasite control methods
Processing Sugar Cane: From Field to Factory
The intricate trip of sugar cane from field to factory includes a number of essential actions that change this lively plant right into a raw material for sugar manufacturing. After gathering, sugar cane is promptly transported to the handling facility to reduce sucrose loss. The primary step at the factory is washing the cane to get rid of contaminations, adhered to by crushing to remove the juice. This juice goes through information, where it is warmed and treated with lime to remove strong particles and impurities.Once made clear, the juice is focused with dissipation, leading to syrup. The syrup is after that taken shape by cooling and including seed crystals, bring about the formation of sugar crystals. Complying with condensation, the sugar undergoes centrifugation to separate it from molasses. Inevitably, the sugar is dried, packaged, and gotten ready for distribution. Each action in this procedure is important for making certain the high quality and performance of sugar manufacturing.
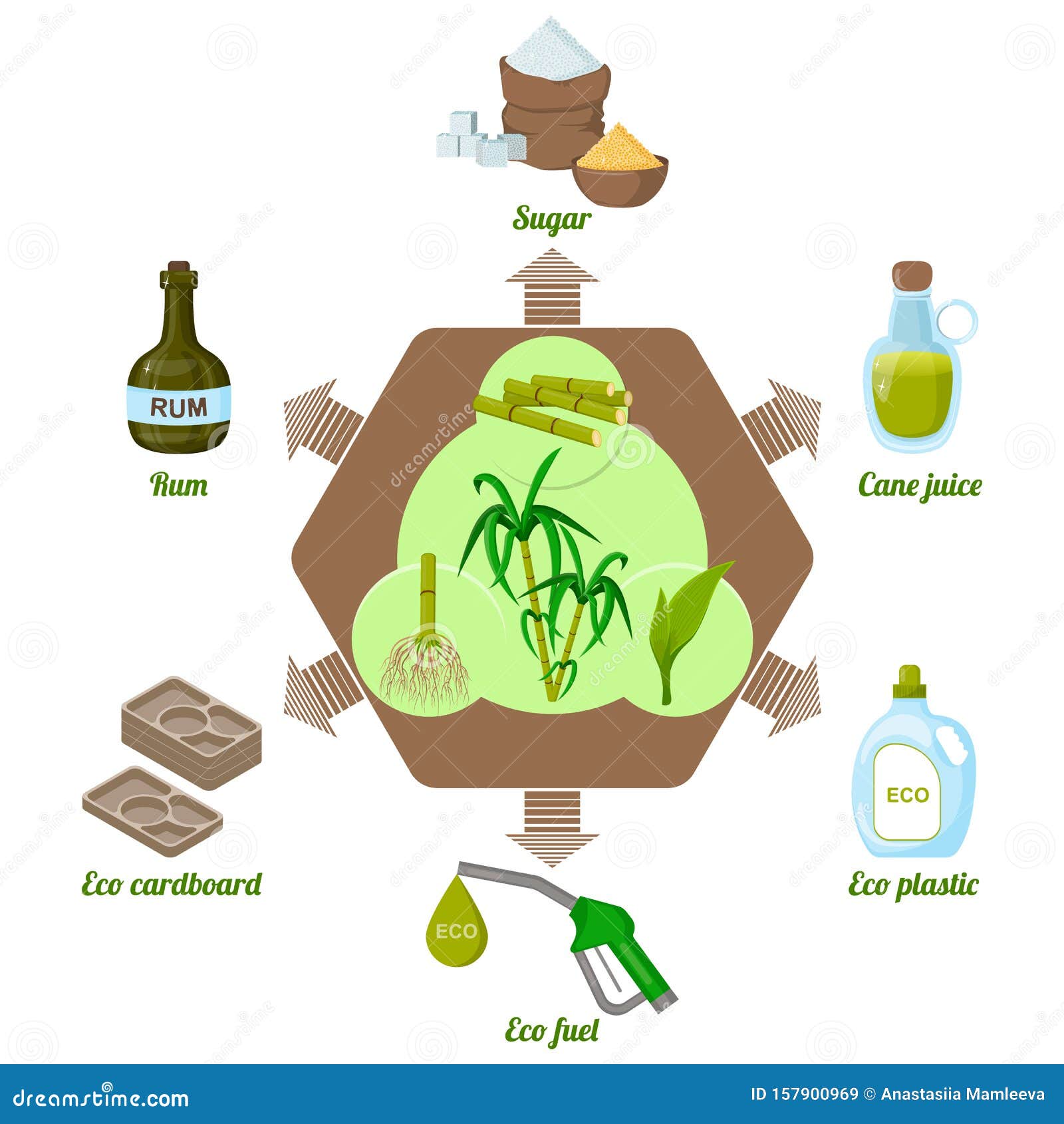
Sugar Cane Products and Their Applications

Sweeteners and All-natural Sugars
Although often forgotten, sugar and all-natural sugars derived from sugar cane play a crucial duty in the food and beverage market. These items, including sucrose, molasses, and raw sugar, give an array of flavors and functionalities that improve various food products. Sucrose, the most common sugar, is commonly used for its sweetening buildings, while molasses contributes deepness and complexity to baked items and sauces. All-natural sugars from sugar cane are preferred for their minimal processing and viewed health advantages contrasted to sweetening agents. On top of that, developments in sugar cane processing have resulted in alternatives like fluid sugar and focused cane juice, dealing with diverse customer choices. In general, sugar cane-derived sweeteners are important to flavoring, protecting, and enhancing food experiences.
Biofuels and Renewable Energy

Sustainability in energy manufacturing has increasingly turned attention to sugar cane as a practical resource for biofuels. This tropical plant, rich in sucrose, can be published here exchanged ethanol, a renewable gas that lowers greenhouse gas emissions compared to fossil fuels. The fermentation process uses molasses, a byproduct of sugar manufacturing, maximizing resource efficiency. Sugar cane's biomass, consisting of bagasse and leaves, can be transformed imp source right into bioenergy, adding to a circular economic climate. Different technologies in processing strategies enhance the yield of biofuels, making sugar cane an appealing choice for energy diversification. Furthermore, the growing demand for lasting energy resources drives research into enhancing growing methods and decreasing the carbon impact of biofuel production, positioning sugar cane as a principal in the sustainable power landscape.
Developments in Sugar Cane Sustainability
As the global need for sugar rises, technologies in sugar cane sustainability have actually come to be important to fulfill both environmental and economic difficulties. Modern agricultural methods are being executed to minimize water usage, boost soil wellness, and decrease chemical inputs. Methods such as precision farming make use of information analytics and technology to maximize source usage and boost plant yields sustainably.Additionally, the advancement of genetically customized sugar cane selections intends to boost resistance to bugs and ecological stressors, leading to higher performance with less inputs. Waste management techniques are also developing; spin-offs from sugar cane handling are being changed into bioenergy, lowering dependence on fossil fuels.Furthermore, partnerships in between farming stakeholders and ecological companies are promoting methods that advertise biodiversity and community health. These advancements not just assist mitigate the environmental impact of sugar cane manufacturing yet also produce a much more resilient and lasting industry for the future.
The Future of Sugar Cane in Global Markets
While international sugar usage proceeds to rise, the future of sugar cane in worldwide markets encounters both opportunities and obstacles. The boosting need for biofuels and sustainable items presents a substantial possibility for sugar cane manufacturers, as the plant can be used for ethanol manufacturing and other environment-friendly alternatives. Furthermore, innovations in handling techniques might boost effectiveness and reduce prices, making sugar cane much more affordable versus other sweeteners.However, obstacles such as environment adjustment, varying market value, and transforming customer choices towards much healthier alternatives make complex the landscape. Profession policies and tolls can affect the international market characteristics, influencing farmers' success. As stakeholders browse these complexities, partnership among manufacturers, governments, and researchers will be vital in adapting to the progressing market. The future of sugar cane hinges on stabilizing these possibilities and obstacles to safeguard its location in a swiftly altering worldwide economic climate.
Regularly Asked Questions
How Does Sugar Cane Impact Citizen Ecosystems and Biodiversity?
The cultivation of sugar cane significantly affects local ecological communities and biodiversity. Monoculture methods can bring about environment devastation, while chemical usage may harm non-target varieties, inevitably disrupting environmental equilibrium and decreasing species richness in affected areas.
What Are the Wellness Results of Consuming Sugar Cane Products?
The health impacts of consuming sugar cane items consist of potential benefits like power increases and antioxidants, however too much consumption might lead to weight gain, dental issues, and enhanced danger of diabetes, urging moderation in consumption.
Exist Any Kind Of Alternatives to Sugar Cane for Sugar Manufacturing?
Alternatives to sugar cane for sugar manufacturing consist of sugar beetroot, maple sap, and coconut palm sap. These resources supply comparable sweet taste and can be grown in different environments, using varied alternatives for sugar production worldwide.
Exactly How Is Sugar Cane Influenced by Environment Adjustment?
Environment change greatly impacts sugar cane, creating altered rains patterns, boosted temperatures, and enhanced bug pressures. These elements why not check here can reduce returns and affect total quality, motivating the need for flexible agricultural techniques to guarantee sustainability.
What Are the Labor Problems for Sugar Cane Workers Worldwide?
Labor problems for sugar cane employees around the world vary significantly, often characterized by low earnings, lengthy hours, and inadequate security procedures. Lots of face exploitation and rough workplace, especially in establishing nations reliant on sugar cane production.
Report this page